-
Mail Us Todaysales@efpcb.com
-
Company LocationShenzhen, Guangdong, China
-
+86-755-23724206Call us for more details
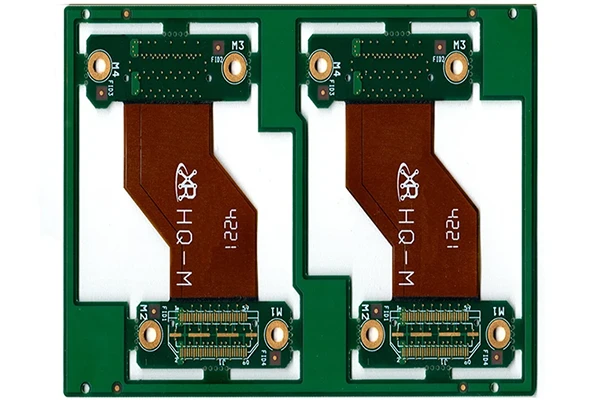

Part No.: E0415060279A
Layer count: 4 layer
Material: FR4 TG170, 1.6mm, high TG +2 mil PI, 1 OZ for all layer
Minimum track: 5 mil
Minimum space(gap): 5 mil
Minimum hole: 0.20mm
Surface finished: ENIG
Panel size: 228*158mm/2up
The rigid-flex PCBs is one of the most flexible and exciting technologies in the printed circuit board (PCB) industry. Hybrid boards that benefit from both rigid and flexible PCB attributes, they are perfect for applications needing small form factors, light weight, and reliability even in environments that have movement and vibration. From aerospace and automotive to consumer electronics and medical equipment, Rigid flex PCB technology is reshaping the way electronic products are designed and produced. This article provides an in-depth review of the fabrication process, the challenges and design guidelines for making rigid-flexible PCBs.
A rigid flex PCB in itself can be described as a rigid PCB board (solid and hard) combined with a flexible section which provides the functional benefits typically associated with a flexible PCB. These boards are essentially rigid panels linked by flexible sheets, allowing for designs that can be folded, twisted, or bent without affecting performance. The stiffness sections carry components that need stability, while the flexible parts provide flexibility and connection between tight spaces. Such hybrid construction is especially useful in applications where space is at a premium, or the mechanics of the system are dynamic.
The rigid flexible PCB manufacturing process is a mixture of those two methods used in rigid PCB and flexible PCB fabrication. Here are the basic steps:
The selection of materials for both rigid and flex layer is the very first amidst the rigid flexible PCB manufacturing process.
The adhesive must be compatible with both materials, have a strong bond, but not compromise electrical performance.
Layer stack-up is crucial in rigid flexible PCB fabrication. It specifies the sequence of the rigid and flex layers in which copper traces, dielectric materials and adhesives may be present. A correct stack-up guarantees the mechanical strength, the electrical performance and flexibility.
Generator of most design flex are multi-layered structure between the rigid layers are flexible layers and electrical connection between the layers done with the aid of vias or plated-through-hole. The stack-up has to be meticulously optimized not to be too flexible or rigid so as to prevent failure coming from any stress point.
Circuit Patterning: The process of fabricating the copper traces that provide the electrical connections within the PCB. This step is executed independently for rigid and flexible layers.
Solid Copper: Copper is etched in the standard subtractive manner, removing the unwanted copper to form the required circuit trace design.
Flexible Films Laser Ablation can be applied for flexible regions of the fabricated structure to enable ultra-precise patterning of circuits without damaging the polyimide substrate.
Lamination for rigid flex PCB production Lamination is an essential process in the fabrication of rigid flex PCBs where the rigid/flex layers are laminated into a sandwich. This process involves exacting alignment of vias and traces match between levels correspond.
The lamination process typically involves:
Equipment with special soft handling is needed to process the fragile flexible layers without creating wrinkles or misalignments.
The solder mask helps shield the PCB board so it won`t oxidize and short-circuit during the assembly process. For the rigid flexible PCB manufacture, as the rigid part, the solder mask is often applied only to the rigid part after the removal of the flexible layers so that the flexible layers will retain flexibility.
The rigid flexible PCB undergoes the test of precision to verify that it performs well. Common testing methods include:
Although there are lots of benefits from rigid flexible PCB technology, there is a plenty of problems too:
Driven by an increasing requirement for rigid flexible PCB technology, manufacturers are moving forward with creative methods to achieve its efficiencies and benefits:
What are some benefits of rigid flexible PCB's?
With Rigid Flexible PCB design you can benefit from both the flexibility of Flex and the durability of rigid boards. They replace connectors, saving space and time for installation and enhancing signal quality.
What is scalping hard/soft PCB manufacturing compare to normal PCB manufacturing?
Conventional PCBs are either rigid or flexible, but rigid flexible PCB manufacturing combines the two, necessitating specialized materials, equipment and processes to join rigid and flexible substrates together in an integrated fashion.
What we use rigid flexible PCB?
Aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, and telecommunications are a few of the industries which use rigid-flexible PCBs because they’re smaller and work in harsh conditions.
Why are Rigid flex PCBs more expensive?
Yes, rigid flexible PCBs are a bit expensive because of more complex manufacturing process and dedicated materials. However, their superior, sometimes critical performance often compensates the much higher price.
What is the future of rigid flex PCB technology?
The development of rigid flexible PCB miniaturization will further, the material, the processing technology needs more progress. Wearable devices, internet of things devices, and high-frequency communication systems are among the applications keeping that innovation happening.
Rigid-flex printed circuit board technology is revolutionizing the electronics industry by creating ultra-compact, lightweight, and reliable designs for various applications. And from the selection of materials and lamination, everything from copper plating to testing of the control is executed with precision and innovation that benefits to the versatility and has made history of these tables. With issues like cost and complexity still to be addressed, progress with materials, equipment and design tools continues to support efforts to extend the use of rigid flexible PCBs. As the industries continue onwards with the trend of the smaller and more capable electronics, flexible-rigid PCB manufacturing will have its place in defining the future of the electronics.