-
Mail Us Todaysales@efpcb.com
-
Company LocationShenzhen, Guangdong, China
-
+86-755-23724206Call us for more details

Part No.: E0215060186A
Layer count: 2 layer SAP flex PCB
Material: Polymide, 0.13mm, 1/3 OZ for all layer
Minimum trace: 2.0 mil
Minimum space (gap): 2.0 mil
Minimum hole: 0.15mm
Surface finished: immersion gold
Panel size: 75*15.5mm/1up
Characteristics: Flexible PCB connector, 1mil Polymide, immersion gold, SAP flex PCB, flex connector for Iphone 15
Flexible PCBs have become an integral part of modern electronics, the enabling factor of these lightweight and compact devices that we love so much. And today, of the various factors of product durability and the various ways to improve it, we’ll be taking a look at the role of the bend radius.
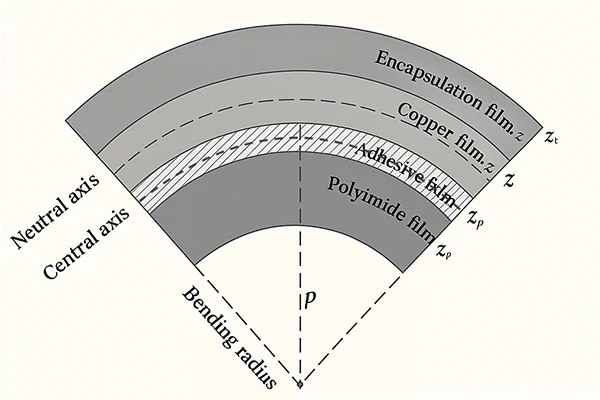
The bend radius is, for a piece of flexible PCB, the radius by which it can bend without suffering mechanical or electrical damage, beyond which the board may crash or even delaminate, and for which the IPC-2223 serve as industry-standard guidelines, specifying the correct bend radius for a given type, thickness and construction.
When a piece of flexible PCB bends within these limits, its internal stresses remain within the material’s limits, allowing for repeated flexes and permanent bends without damage to the board. But if you were to push beyond these limits, you will end up with:
Getting the bend radius right improves reliability and ultimately reduces warranty claims and downtime, especially with more important flexible PCB applications such as wearables, medical devices and aerospace systems.
The minimum bend radius for a given piece of flexible PCB depends on several factors:
The rule of thumb for flexible PCBs from IPC-2223 is:
Here are some tips for maximizing the lifespan of your flexible PCBs:
The various testing methods for flexible PCB that have been standardized across the industry are:
The bend radius is an important consideration in the design for your flexible PCB, and one of the determining variables of its lifespan. In our article today we enumerated the most important factors that decide this bend radius: the thickness, the number of layers, the type of copper and the type of construction, and the amount of flexing that flexible PCB will end up seeing. Remember to take into consideration this important value in your flexible PCB project and we look forward to seeing you next time.
What is the minimum bend radius for a generic piece of flexible PCB?
For a single-layer flexible PCB in a static application, the minimum bend radius would be 6 times its overall thickness. For dynamic flexing, it will have to be 100 times or more.
What happens if I exceed minimum bend radius?
Exceeding the minimum bend radius will result in copper cracking, even delamination, and ultimately in early circuit failure.
How can I test if my flexible PCB design meets bend radius requirements?
Use visual inspections, bend cycle testing, and then electrical continuity tests. These tests will be able to verify whether your product can indeed execute the minim bend radius that you got on paper.
Iphone 15 Flexible PCB Connector